Embracing Efficiency: The Advantages of Heat Pump Water Heaters Over Traditional Systems
In the quest for more sustainable and cost-effective home appliances, heat pump water heaters (HPWHs) are gaining popularity as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional gas and electric resistance (element) hot water systems. This comprehensive look at heat pump technology will delve into why these systems are an advantageous investment for homeowners looking to reduce both their carbon footprint and their utility bills.
Introduction to Heat Pump Water Heaters
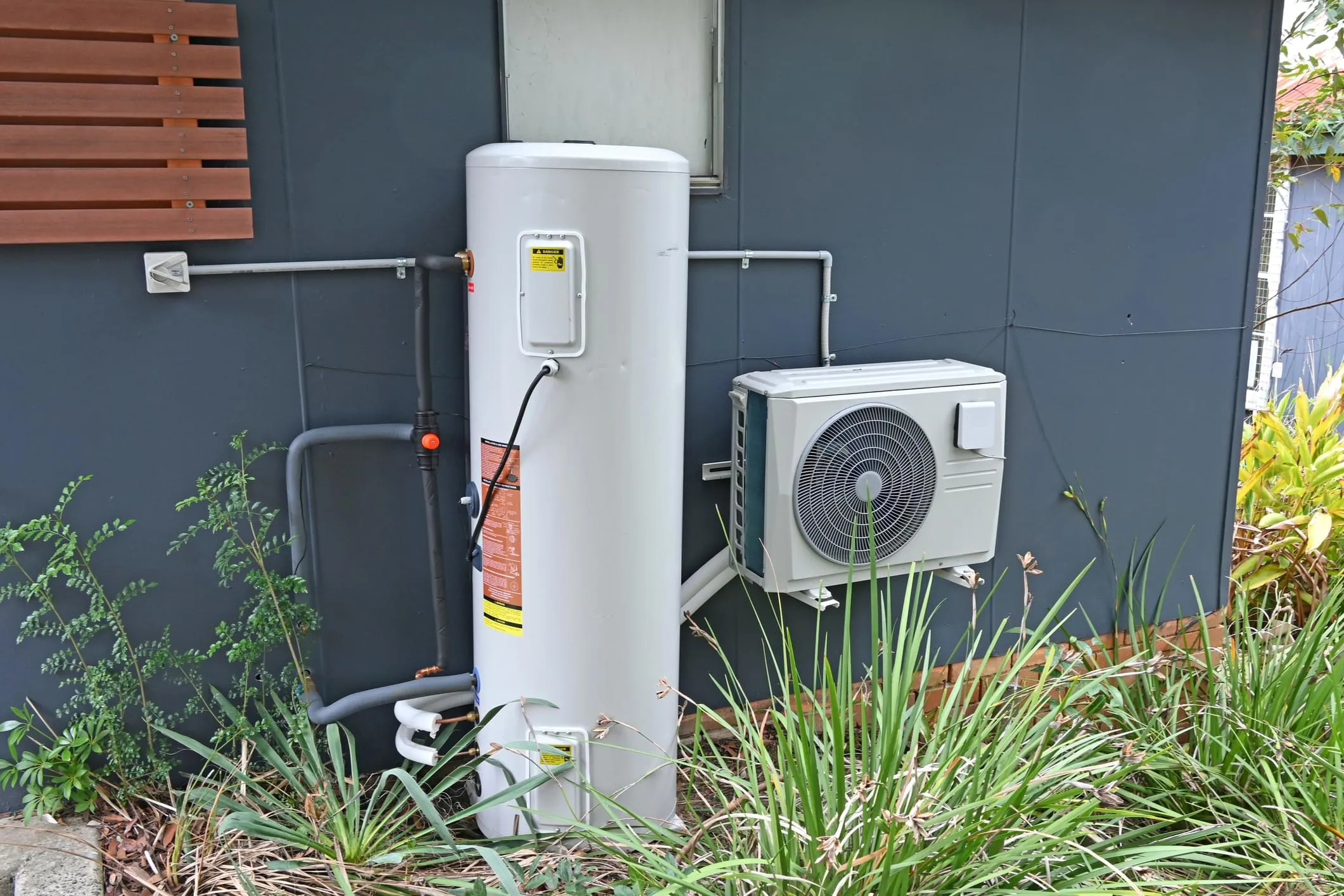
Heat pump water heaters operate on a simple yet efficient principle: rather than generating heat directly, they use electricity to move heat from one place to another. This process is akin to how a refrigerator works, but in reverse. While a refrigerator expels heat from its interior to keep the inside cool, a heat pump water heater pulls heat from the surrounding air into the water tank to heat the water.
How Heat Pumps Work
The core components of a heat pump water heater include a heat exchanger, a compressor, and a refrigerant. The system absorbs ambient heat from the air through the heat exchanger and uses the compressor to increase the temperature of the heat. This heated refrigerant then transfers its heat to the water in the tank. Because they utilize ambient heat and intensify it, heat pumps can operate effectively even in cooler climates, albeit with some efficiency loss as temperatures drop.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
One of the most compelling reasons to choose a heat pump water heater is its superior energy efficiency. HPWHs can be up to three to four times more efficient than traditional water heaters that rely on fossil fuels or electricity for direct heating.
Energy Savings
The efficiency of heat pumps translates into significant energy savings. By moving heat rather than generating it, HPWHs consume less electricity compared to the high amounts required by electric resistance heaters. This can lead to a substantial reduction in energy bills, despite the higher initial cost associated with purchasing and installing a heat pump.
Reduced Carbon Footprint
For environmentally conscious homeowners, heat pumps offer a significant advantage in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike gas water heaters that burn natural gas or propane, contributing to carbon dioxide emissions, heat pumps utilize electricity, which can be sourced from renewable energy. This makes them an ideal choice in regions increasingly transitioning to green power grids.
Cost Implications
While the upfront cost of a heat pump water heater is generally higher than that of traditional water heaters, the long-term savings on energy bills can offset this initial investment. Additionally, many governments and utility companies offer rebates and incentives to reduce the purchase and installation cost of energy-efficient appliances like HPWHs.
Long-Term Savings
Over the lifespan of the unit, which can be significantly longer than that of traditional water heaters, the cumulative savings from reduced energy use can add up to more than the price difference. This makes heat pumps an economically wise choice in the long run.
Maintenance and Durability
Heat pump water heaters typically have a longer lifespan compared to traditional gas water heaters. They are also generally less maintenance-intensive since they do not involve combustion processes, thus eliminating the need to manage exhaust and the potential safety risks associated with gas leaks and carbon monoxide.
Safety and Convenience
From a safety perspective, HPWHs provide peace of mind by eliminating the risks associated with gas leaks and carbon monoxide poisoning, common concerns with fossil-fuel-based systems. They also offer the convenience of easier integration with existing electrical systems in homes, avoiding the need for gas lines and venting infrastructure.
Versatility and Additional Benefits
Modern heat pump systems can be integrated into home heating and cooling systems to provide not just hot water but also assist with regulating indoor temperatures. This dual functionality makes heat pump systems a versatile addition to homes, optimizing energy use across multiple functions.
Conclusion
Choosing a heat pump water heater over traditional gas or electric models is a wise decision for the environmentally conscious and cost-aware homeowner. The benefits of HPWHs—ranging from greater energy efficiency and lower operating costs to reduced environmental impact and enhanced safety—make them a compelling choice for those looking to modernize their home’s heating systems.
As the world moves towards more sustainable energy solutions, heat pump technology stands out as a practical and forward-thinking option that aligns with both economic and environmental goals. Homeowners are encouraged to consider the long-term benefits and potential savings when deciding on their next water heating system.